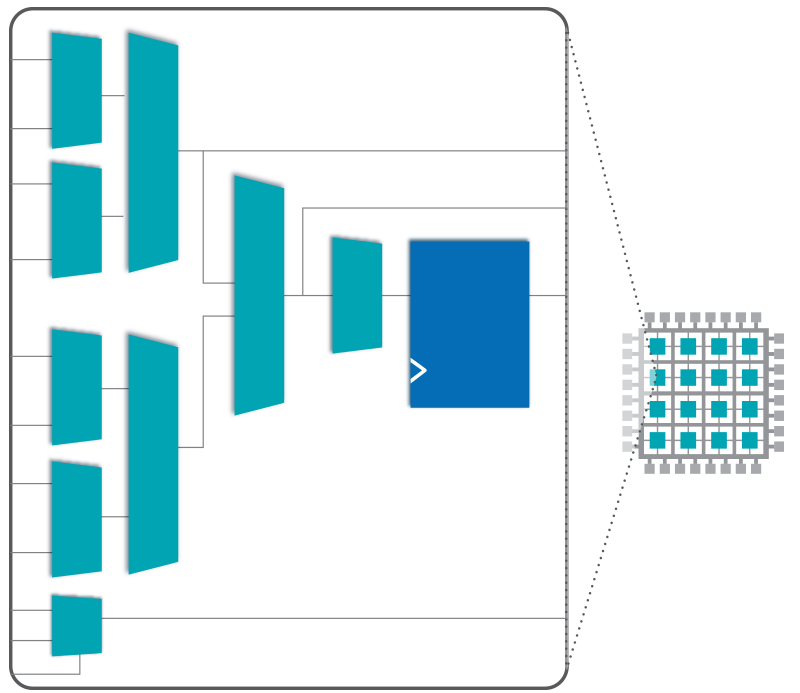
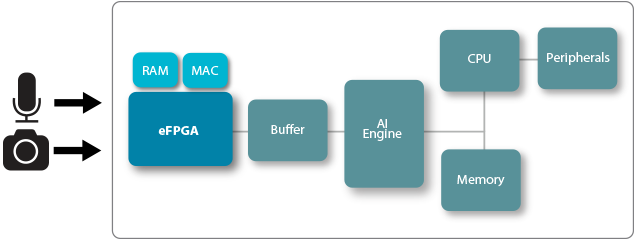
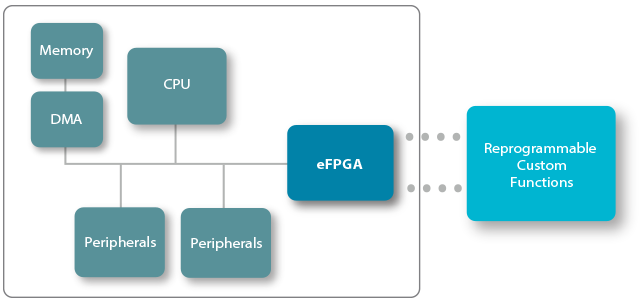
eFPGA is an ideal platform for updating and changing functions / algorithms, especially for systems that are deployed in the field where access is difficult
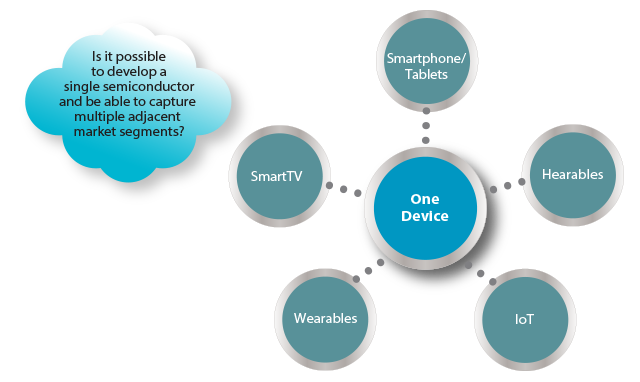
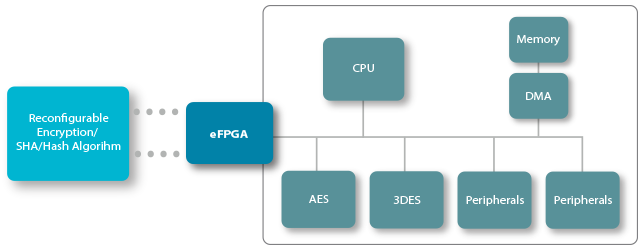
Common security algorithms can be implemented as hardened functions, but customers often prefer to have their own security algorithm on top of common security algorithms in order to make their application more secure.